
Chromecast Extension For Firefox PC Archives

Chromecast Extension For Firefox PC Archives
Firefox for Android
 | |
 | |
| Developer(s) | |
|---|---|
| Stable release(s)[±] | |
| 80.0 (August 31, 2020; 14 days ago (2020-08-31)[1]) [±] | |
| Preview release(s)[±] | |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C++, XUL, Java, JavaScript, Rust |
| Operating system | Android 5.0 and above[7] |
| Size | |
| Type | Mobile browser |
| License | MPL |
| Website | https://www.mozilla.org/firefox/mobile/ |
Firefox for Android (codenamed Fenix, formerly codenamed Fennec) is a free and open-sourceweb browser developed by Mozilla for Androidsmartphones and tablet computers. Firefox for Android uses the GeckoViewengine.
From 2010 to 2011, the Fennec project additionally supported Maemo phones. Mozilla also makes another mobile browser for iOS called Firefox for iOS.
History[edit]
Firefox for mobile, codenamed "Fennec", was first released for Maemo in January 2010 with version 1.0[12] and for Android in March 2011 with version 4.0.[13] Support for Maemo was discontinued after version 7, released in September 2011.[14] The codename Fennec comes from the fennec fox, a small desert fox (just as the Fennec browser is a small version of the Firefox desktop browser). Firefox for Maemo Beta 5, released in 2009, was the first version to have the official Firefox branding, with the Firefox name and logo.[15]
Fennec uses the Gecko engine; for example, version 1.0 used the same engine as Firefox 3.6, and the following release, 4.0, shared core code with Firefox 4.0. Its features include HTML5 support, Firefox Sync, add-ons support and tabbed browsing.[16] The browser's version numbering was bumped from version 2.0 beta to version 4.0 to more closely match desktop releases of Firefox since the rendering engines used in both browsers are the same.[17]
Plugin support was initially disabled by default, removing compatibility with popular web content types such as Adobe Flash.[18] In September 2011, Flash support was implemented in pre-release builds for pre-Honeycomb versions of Android.[19] Flash support for Android 2.x and 4.x was enabled for most smartphones in version 14.0;[20] later it was removed in version 56.0.[21]
The last version of Fennec was version 68, released in July 2019, receiving bug and security fixes until July 2020.[22][23][24]
On June 27, 2019, Mozilla unveiled Firefox Preview (codename "Fenix"), a redesigned version of Firefox for Android based on the GeckoView engine — an implementation of Gecko that is decoupled as a reusable library, intended to be used as an alternative to the default Android WebView component.[25][26] Firefox Beta was migrated to Fenix in April 2020,[27] and it was officially released to stable in August 2020 as version 79, branded as Firefox Daylight. It includes the Enhanced Tracking Protection features from the desktop version, defaulting to an address bar along the bottom of the screen, support for dark mode, a new "Collections" feature, and a redesigned private browsing mode based on Firefox Focus.[28][29]
Add-ons[edit]
Firefox for Android allows installation of extensions; due to the change in architecture and the need to ensure that they are properly optimized for mobile use, Firefox Daylight/"Fenix" only supports a curated selection of popular extensions from the Mozilla Add-ons "Recommended Extensions" program, with only nine (Dark Reader, Decentraleyes, HTTPS Everywhere, NoScript, Privacy Badger, Privacy Possum, Search by Image, uBlock Origin, and YouTube High Definition) supported on-launch, and at least 30 to be supported by the end of 2020.[30][29]
Platforms[edit]
Firefox for Android, starting with Version 79 from July 2020, only runs on Android version 5.0 and later; earlier versions of Firefox also supported earlier versions of Android.[7] Support for Android devices that run Intel x86 processors was added in December 2013.[31]
Previously or unofficially supported[edit]
Previously, Firefox for mobile supported other platforms besides Android.
Official support for the Nokia N900Maemo device ceased with version 7.[32]
Firefox mobile was available for MeeGo through the third-party OpenRepos repository.[33]
An alpha build of version 1.1 (1.1 Alpha 1) for Windows Mobile, released on February 19, 2010, is the last build for this operating system.[34][35] Following the Windows Phone 7 announcement and Microsoft's decision not to release a native development kit, as with Android and other systems, development for Windows Mobile was put on hold.[36] If Microsoft releases a native development kit in the future for its Windows Phone OS, then Mozilla will consider again developing Fennec for the platform.[37]
Tristan Nitot, president of Mozilla Europe, has said that it's unlikely that a BlackBerry OS version will be released, citing BlackBerry's limited operating system as the reason.[38] Mozilla has no plans to develop Firefox for the Symbian platform,[37] or webOS.[37] An unofficial port to WebOS was made, but is no longer maintained as of 2011.[39]
An unofficial port is available for the Pandora handheld console.[40]
Firefox 52.0.2 was the last version to run on ARM devices without NEON support, such as those with Tegra 2.[41][42]
| Operating system | Latest stable version | Support status | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android (including Android-x86) | 5.0 and later | Current stable version:80.0 (x64)[43] | 2018– |
| Current stable version:80.0 (ARM64)[43] | 2017– | ||
| Current stable version:80.0 (IA-32 and ARMv7)[43] | 2014– | ||
| 4.1–4.4 | Old version, no longer maintained:68.11.0 (x64)[44] | 2018–2020 | |
| Old version, no longer maintained:68.11.0 (IA-32) | 2013–2020 | ||
| Old version, no longer maintained:68.11.0 (ARMv7) | 2012–2020 | ||
| 4.0 | Old version, no longer maintained:55.0.2 (IA-32)[45][46] | 2013–2017 | |
| Old version, no longer maintained:55.0.2 (ARMv7) | 2011–2017 | ||
| 3.0–3.2 | Old version, no longer maintained:45.0.2 (ARMv7)[45] | 2011–2016 | |
| 2.3 | Old version, no longer maintained:47.0 (ARMv7)[45][47] | ||
| 2.2–4.3 | Old version, no longer maintained:31.3.0esr (ARMv6) | 2012–2015 | |
| 2.2 | Old version, no longer maintained:31.0 (ARMv7)[48] | 2011–2014 | |
| 2.1 | Old version, no longer maintained:19.0.2 (ARMv6) | 2012–2013 | |
| Old version, no longer maintained:19.0.2 (ARMv7) | 2011–2013 | ||
| 2.0 | Old version, no longer maintained:6.0.2 (ARMv7) | 2011 | |
| Firefox OS | 2.2 | Old version, no longer maintained:35/36/37 | 2015 |
| 2.1 | Old version, no longer maintained:33/34 | 2014–2015 | |
| 2.0 | Old version, no longer maintained:31/32 | ||
| Maemo | Old version, no longer maintained:7.0.1 | 2010–2011 | |
- Notes
- Firefox for iOS is not listed in this table as its version numbers would be misleading; it uses version numbers that do not correspond to any of the other Firefox versions. Those share a core component, the Gecko rendering engine, and track its version numbers, whereas the version for the iOS operating system uses the operating system's rendering engine (WebKit), rather than Mozilla's (Gecko).
Reception[edit]
 | This article needs to be updated. Please update this section to reflect recent events or newly available information.(August 2020) |

The main criticisms[by whom?] of the browser pre-version 14 were slow browsing speed, lack of plugin support and performance issues.[49][50] To address these concerns, Mozilla redesigned the browser in version 14.0, adding Flash support, improving start-up speed, as well as other enhancements.[51] This update dramatically improved Firefox for Android. As of September 2014[update], the average user rating of Firefox for Android on the Google Play Store is 4.4.[52]
Compared to the stock Android browser and Chrome on Android, Firefox has a small market share; for the month of November 2015, Firefox for Android usage share of all mobile/tablet browsers was just 0.81%.[53] Despite that, Firefox for Android enjoys a high Play Store rating, has over 100 million downloads,[54][55] and continues to be developed. The latest version supports Android 4.0 and higher (as Android 2.3 support was dropped in version 48).[56]
In its 2015 Android browser comparison, Spanish software news and reviews site Softonic.com awarded Firefox version 37.0.1 the Best of 2015 nod, with reviewer Fabrizio Benedetti citing a good design, efficient memory consumption, the browser's open source nature, and independence.[55]
In August 2020, Mozilla released a major update of Firefox for Android, version 79, which had been in development for more than 1 year with the codename "Firefox Daylight". It was described by Mozilla as being "dramatically redesigned to be faster, easy to use, customizable and private".[57] However, it received intense criticism from users, who complained that it was more difficult to use, and slower, and various features were suddenly missing. Some online Tech Writers even recommended people to disable the update if possible.[58][59][60][61][62][63]
Security advantages[edit]
A number of devices run older versions of Android.[64] Some would not be upgraded to newer versions because of insufficient technical knowledge by users, or their lack of access to mobile data; some devices cannot be upgraded because of low system resources, or the manufacturer and telecoms operator have failed to provide an update.[citation needed]
As of early 2015, Google has stopped issuing its own patches for Android 4.3 and earlier to the WebView browser component and the WebKit rendering engine therein, which are used by the native/stock and often default AOSP browser in a large number of Android devices – thereby shifting the patching responsibility to device manufacturers.[65] In time, the native browser or browser components become outdated, increasingly insecure, and unable to properly render modern websites.[66]
As a workaround, a Google engineer suggested using the separately-installable and updateable Google Chrome or Firefox browsers.[65] In case of Ice Cream Sandwich (4.0.x), Google stopped supporting that branch of Android with updates to its Chrome browser after Chrome 43, and moved up to Android 4.1 as the oldest release supported by Google Chrome.[56][66]
The open-source nature of Firefox has made it possible to maintain its development for operating system versions that are past their product support life cycle, and has resulted in Firefox having stronger security and better support for modern web standards.[citation needed] This in effect extends the useful lifetime of devices stuck on older major versions of Android.[citation needed]
Similar to the desktop Firefox: Version 60 introduces the setting DNS over HTTPS and has to be activated manually in about:config.[67]


Forks and code reuse[edit]
IceCatMobile[edit]
GNU maintains a fork of the latest long-term (so-called "ESR") version of Firefox for Android, with all proprietary binaries removed.[68]
Fennec F-Droid[edit]
On 1 February 2015 and beginning with version 35.0,[69] the open-source F-Droid app repository hosts the Fennec F-Droid package. This is a FOSS-only version of the browser, pulled from the unbranded Firefox source code, licensed under MPL2, and based on the latest (that is, non-long-term) Firefox releases. Part of the package's name comes from the mobile Firefox's Fennec code name.
Maintainers of this version strive to keep out all proprietary binaries used in Firefox, but some might still remain.[70] As of version 38.0.5, the following items have been removed:
- Tests;
- Crash reporter;
- Health reporter;
- Media streaming (requires the non-free play-services library);
- Updater;
- Encrypted Media Extensions (EME) / DRM.
Adblock Browser[edit]
On 20 May 2015, Eyeo GmbH, the maintainers of Adblock Plus, released Adblock Browser 1.0 beta, which is based on Firefox for Android.[71] The browser uses a similar blocking/permitting model as Adblock Plus, allowing by default ads deemed "acceptable" by Eyeo. A major drawback compared to Firefox for Android is Adblock Browser's lack of support for Firefox Sync.
Initial reviews have been mixed: On one hand, users would be happy to have less ads and resource consumption on their devices; on the other hand, web services, publications, content creators and bloggers rely on advertisements for their revenue and income.[72][unreliable source?]
Adblock Browser 1.0 was released on 7 September 2015. It's compatible with Android 2.3 or greater, and has about the same system requirements as Firefox for Android.[73]
Orfox[edit]
On 30 June 2015, The Guardian Project announced a stable alpha of Orfox, the new mobile counterpart of the Tor Browser. Orfox is built from Fennec (Firefox for Android) code and the Tor Browser code repository, and is given security hardening patches by the Tor Browser development team. Some of the Orfox build work is based on the Fennec F-Droid project.[74]
The project removed in Orfox the WebRTC component and Chromecast connectivity, and app permissions to access the camera, microphone, contacts (address book), location data (GPS et al.), and NFC.[74][75]
Orfox is to supersede the Orweb browser project, which used the WebView engine.[74]
LibreOffice[edit]

Firefox for Android (Fennec)'s front-end code was taken as a base for the new development in the LibreOffice project for Android (along with the pre-existing cross-platform LibreOffice document engine).[76][77] Further work made that Fennec code the core component of LibreOffice Viewer for Android,[78] which was released on 28 May 2015[79] for Android 4.0 or newer.[77]
Release history[edit]
Release dates:
- Version 1: January 28, 2010. For Maemo.[80]
- Version 4: March 29, 2011. For Android and Maemo; version number matched with the desktop version.[13]
- Version 5: June 21, 2011. For Android,[81] supports Android 2.0 and higher.[82]
- Version 6: August 16, 2011.[83]
- Version 6.0.1: August 30, 2011.[84]
- Version 6.0.2: September 6, 2011. Last version for Android 2.0.[85]
- Version 7.0: September 27, 2011.[86] Supports Android 2.1 and higher.[87]
- Version 7.0.1: September 30, 2011. Last version for Maemo.[88]
- Version 8.0: November 8, 2011.[89]
- Version 9.0: December 21, 2011.[90]
- Version 10.0: January 31, 2012.[91]
- Version 10.0.1: February 10, 2012.[92]
- Version 10.0.2: February 17, 2012. Last version available for desktop systems.[93]
- Version 10.0.3: March 13, 2012.[94]
- Version 10.0.4: April 24, 2012.[95]
- Version 10.0.5: June 5, 2012.[96]
- Version 14.0: June 26, 2012, version number matched with the desktop version, first version to support Adobe Flash.[97]
- Version 15.0: August 28, 2012.[98]
- Version 15.0.1: September 10, 2012.[99]
- Version 16.0: October 9, 2012.[100]
- Version 16.0.1: October 11, 2012.[101]
- Version 17: November 19, 2012.[102]
- Version 18: January 8, 2013.[103]
- Version 18.0.2: February 7, 2013.[104]
- Version 19.0: February 19, 2013.[105]
- Version 19.0.2: March 7, 2013. Last version to support Android 2.1.[106]
- Version 20.0: April 2, 2013. Supports Android 2.2 or newer.[107]
- Version 20.0.1: April 11, 2013.[108]
- Version 21.0: May 14, 2013.[109]
- Version 22.0: June 25, 2013.[110]
- Version 23.0: August 6, 2013.[111]
- Version 24.0: September 17, 2013.[112]
- Version 25.0: October 29, 2013.[113]
- Version 25.0.1: November 15, 2013.[114]
- Version 26.0: December 10, 2013.[115]
- Version 26.0.1: December 20, 2013.[116]
- Version 27.0: February 4, 2014.[117]
- Version 28.0: March 18, 2014.[118]
- Version 28.0.1: March 24, 2014.[119]
- Version 29.0: April 29, 2014.[120]
- Version 29.0.1: May 9, 2014.[121]
- Version 30.0: June 10, 2014.[122]
- Version 31.0: July 22, 2014. Last version to support Android 2.2 and ARMv6 chipset; security updates were released through January 2015.[123]
- Version 32.0: September 2, 2014, added support for Firefox OS.[124]
- Version 32.0.1: September 10, 2014.[125]
- Version 32.0.3: September 24, 2014.[126]
- Version 33.0: October 13, 2014.[127]
- Version 33.1: November 10, 2014,[128] celebrating Firefox's 10 year Anniversary.[129]
- Version 34.0: December 1, 2014.[130]
- Version 34.0.1: December 19, 2014.
- Version 35.0: January 13, 2015.[131]
- Version 35.0.1: February 5, 2015.[132]
- Version 36.0: February 27, 2015.[133]
- Version 36.0.1: March 6, 2015.[134]
- Version 36.0.2: March 16, 2015.[135]
- Version 36.0.3: March 20, 2015.[136]
- Version 36.0.4: March 21, 2015.[137]
- Version 37.0: March 31, 2015.[138] Split releases between API levels for Android 2.3 / 3.0 and newer.[139]
- Version 37.0.1: April 3, 2015.[140]
- Version 37.0.2: April 14, 2015.[141]
- Version 38.0: May 12, 2015.[142]
- Version 38.0.5: June 2, 2015.[143]
- Version 39.0: July 2, 2015.[144]
- Version 40.0: August 11, 2015.[145]
- Version 40.0.3: August 27, 2015.[146]
- Version 41.0: September 22, 2015.[147]
- Version 41.0.2: October 15, 2015.[148]
- Version 42.0: November 3, 2015.[149]
- Version 43.0: December 15, 2015.[150]
- Version 44.0: January 26, 2016.[151]
- Version 44.0.2: February 11, 2016.[152]
- Version 45.0: March 8, 2016.[153]
- Version 45.0.1: March 16, 2016.[154]
- Version 45.0.2: April 11, 2016. Last version to support Android 3.x.[155]
- Version 46.0: April 26, 2016.[156]
- Version 46.0.1: May 3, 2016.[157]
- Version 47.0: June 7, 2016. Last version to support Android 2.3.x.[158]
- Version 48.0: August 2, 2016.[159]
- Version 49.0: September 20, 2016.[160]
- Version 49.0.2: October 20, 2016.[161]
- Version 50.0: November 15, 2016.[162]
- Version 50.0.2: November 30, 2016.[163]
- Version 50.1.0: December 13, 2016.[164]
- Version 51.0: January 24, 2017.[165]
- Version 51.0.2: February 6, 2017.[166]
- Version 51.0.3: February 9, 2017.[167]
- Version 52.0: March 7, 2017.[168]
- Version 52.0.1: March 17, 2017.[169]
- Version 52.0.2: March 28, 2017.[170]
- Version 53.0: April 19, 2017.[171]
- Version 53.0.1: April 27, 2017.[172]
- Version 53.0.2: May 5, 2017.[173]
- Version 54.0: June 13, 2017.[174]
- Version 54.0.1: June 29, 2017.[175]
- Version 55.0: August 8, 2017.[176]
- Version 55.0.2: August 16, 2017. Last version to support Android 4.0.x and Adobe Flash.[177][21]
- Version 56.0: September 28, 2017.[21]
- Version 57.0: November 14, 2017. First version based on Quantum project.[178]
- Version 57.0.1: November 29, 2017.[179]
- Version 57.0.4: January 4, 2018.[180]
- Version 58.0: January 23, 2018.[181]
- Version 58.0.1: January 29, 2018.[182]
- Version 58.0.2: February 7, 2018.[183]
- Version 59.0: March 13, 2018.[184]
- Version 59.0.1: March 16, 2018.[185]
- Version 59.0.2: March 26, 2018.[186]
- Version 60.0: May 9, 2018.[187]
- Version 60.0.1: May 16, 2018.[188]
- Version 60.0.2: June 6, 2018.[189]
- Version 61.0: June 26, 2018.[190]
- Version 61.0.2: August 8, 2018.[191]
- Version 62.0: September 5, 2018.[192]
- Version 62.0.1: September 7, 2018.[193]
- Version 62.0.2: September 21, 2018.[194]
- Version 62.0.3: October 2, 2018.[195]
- Version 63.0: October 23, 2018.[196]
- Version 63.0.2: November 7, 2018.[197]
- Version 64.0.1: December 14, 2018.[198]
- Version 64.0.2: January 9, 2019.[199]
- Version 65.0: January 29, 2019.[200]
- Version 65.0.1: February 12, 2019.[201]
- Version 66.0: March 19, 2019.[202]
- Version 66.0.1: March 22, 2019.[203]
- Version 66.0.2: March 27, 2019.[204]
- Version 66.0.4: May 5, 2019.[205]
- Version 66.0.5: May 7, 2019.[206]
- Version 67.0: May 21, 2019.[207]
- Version 67.0.2: June 11, 2019.[208]
- Version 67.0.3: June 18, 2019.[209]
- Version 68.0: July 9, 2019.[210]
- Version 68.0.2: August 14, 2019.[211]
- Version 68.1: September 3, 2019.[212]
- Version 68.1.1: September 13, 2019.[213]
- Version 68.2.0: October 22, 2019.[214]
- Version 68.2.1: November 13, 2019.[215]
- Version 68.3.0: December 3, 2019.[216]
- Version 68.4.0: January 7, 2020.[217]
- Version 68.4.1: January 8, 2020.[218]
- Version 68.4.2: January 20, 2020.[219]
- Version 68.5.0: February 11, 2020.[220]
- Version 68.6.0: March 10, 2020.[221]
- Version 68.7.0: April 7, 2020.[222]
- Version 68.8.0: May 5, 2020.[223]
- Version 68.8.1: May 11, 2020.[224]
- Version 68.9.0: June 2, 2020.[225]
- Version 68.10.0: June 30, 2020.[226]
- Version 68.10.1: July 7, 2020.[227]
- Version 68.11.0: July 27, 2020. Last version to support Android 4.1–4.4.[228]
- Version 79.0: August 27, 2020.[229]
- Version 80.0: August 31, 2020.[230]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
jagan605 said
Sorry to bump this but I can't find the about:config switch
Once you're on the 'about:config' page, type in the search bar : browser.casting. and then look for that preference.
the alternative that I could find that works in Mac and Linux is mkchromecast .
The OP is on Windows ....... But this may be helpful to users who are on Mac or Linux, so : thank you !
Mozilla’s Firefox is one of those web browsers who is working to fight the dominance of Google Chrome and Chromium engine on the Internet. Gecko engine is the one used by Mozilla Firefox while Google Chrome uses Chromium. Even Microsoft has announced moving Microsoft Edge from the EdgeHTML engine to Chromium as well. Running on Gecko, Mozilla Firefox does not get native support for Google’s Chromecast. But people have been working hard to bring in support for Chromecast on Mozilla Firefox. A developer has built a Firefox Extension called Fx_cast which fulfills the missing Chromecast capabilities.
Add Chromecast support to Firefox
Support for Chromecast casting on a web browser brings in the capability to a web browser to cast media files to a Chromecast compatible device like a TV, Media TV Stick or a Smart speaker like a Google Home speaker.
This extension is currently in a very early beta development stage. But can be used properly with Netflix and YouTube. It is available for Mozilla Firefox on Windows, Linux as well as MacOS.
Install Fx_cast on Firefox
The latest releases for it are available on Matt Hensman’s page here.
You need to download the Bridge file for your respective operating system and the Mozilla Firefox extension file too. Now, you need to install the Bridge first.
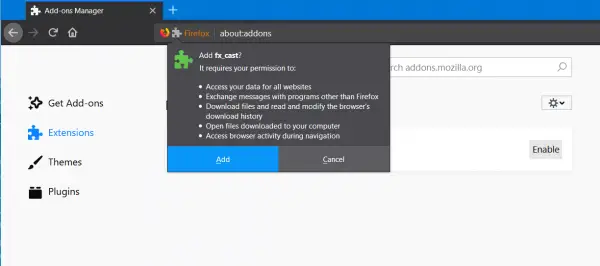
Once that is done, open Mozilla Firefox. In the address bar, type in the following and hit Enter: about:addons
On the left side navigation panel, select Extensions.
On the right side panel, click on the gear icon and select Install Add-on from a file… It will open a mini File Explorer where you need to select the downloaded XPI file.
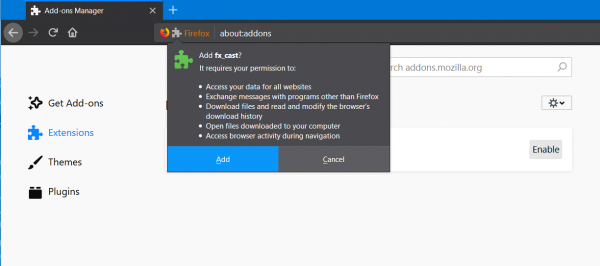
You will now be prompted to install the Add-on on Mozilla Firefox as shown in the snippet above. Select Add in the mini window.
This installs the extension on your copy of Mozilla Firefox.
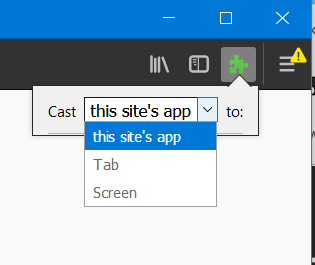
Now, you can cast your site’s application, tab or the screen by selecting the extension’s icon from the top right portion of the Mozilla Firefox web browser as shown in the screen snippet above.
Did you find this extension helpful?
What’s New in the Chromecast Extension For Firefox PC Archives?
Screen Shot
System Requirements for Chromecast Extension For Firefox PC Archives
- First, download the Chromecast Extension For Firefox PC Archives
-
You can download its setup from given links:


