
Mac & Linux Archives

Mac & Linux Archives
How to remove files from ZIP Archives in macOS and Linux
When ZIP up directories, particularly on macOS, some files may find their way into our ZIP archives that were never meant to be there. I’m thinking of those pesky .DS_Store and __MACOSX files, maybe even .htaccess files. For *nix based systems, * really means “everything”.
The ZIP command line tool let us remove such unwanted files from an existing archive. Here’s how:
zip -d your-archive.zip file1 file2The -d switch tells ZIP to hunt for and delete the unwanted files. Files whose names contain spaces can be defined in “regular quotes”, and the * asterisk can be used as usual.
For example, to remove all DS_Store files and __MACOSX files, we can use this:
zip -d your-archive.zip "__MACOSX*" DS_Store*To verify that such idiosyncrasies have indeed been removed from a ZIP archive before we release it into the wide, we can check with the UNZIP utility:
unzip -l your-archive.zipThis will simply list the contents of your-archive.zip without actually extracting it.
Open/Extract xar/pkg File with Freeware on Windows/Mac/Linux
xar (short for eXtensible ARchive) is an open source file archiver and the archiver¡¯s file format. It was created within the OpenDarwin project and is used in Mac OS X 10.5 for software installation routines, as well as browser extensions in Safari 5.0. Xar replaced the use of gzipped pax files.
pkg is just .xar archives with a different extension and a specified file hierarchy. pkg is an OS X Installer file. This file format is used by Apple Inc. on its Macintosh line of computers and on the iPhone. It is also used by Sony PlayStation 3 on downloadable content over PlayStation Network. The contents of a PKG file can be installed using the Apple Installer application.
The XAR project aims to provide an easily extensible archive format. Important design decisions include an easily extensible XML table of contents for random access to archived files, storing the toc at the beginning of the archive to allow for efficient handling of streamed archives, the ability to handle files of arbitrarily large sizes, the ability to choose independent encodings for individual files in the archive, the ability to store checksums for individual files in both compressed and uncompressed form, and the ability to query the table of content's rich meta-data.
The XAR file format has three main regions, The Header, The Table of Contents, and The Heap. The header is a small binary data structure that identifies the file format (file magic). The table of contents is parsed as an XML document. The heap occupies the remainder of the file. Files' data are stored in the heap.
Files in xar are individually compressed. This allows for quick extraction of individual files without the extra disk space requirements and CPU usage of extracting the entire archive, as compared to a compressed tar archive. This makes xar useful for quick restores of accidentally deleted or overwritten files, from a backup archive. Additionally, this means xar can use different compression methods for each file in the archive. For instance, it might not be a good idea to try to try to compress an already compressed file, but a large file might benefit greatly from using bzip2, whereas a small text file would be better served to use gzip.
Open/Extract xar/pkg File on Windows
Easy 7-Zip opens/extracts xar/pkg file easily on Windows. The Easy 7-Zip was developed based on 7-Zip. 7-Zip is a famous open source file archiver. The Easy 7-Zip is an easy-to-use version of 7-Zip. The open source freeware keeps all features of 7-Zip and adds a few useful features that makes the software more user-friendly.
Easy 7-Zip works on Windows 10/8.1/8/7/Vista/2008/2003/XP/2000 (both 32-bit and 64-bit compatible).
- Free Download Easy 7-Zip
- Install Easy 7-Zip by step-by-step instructions
- The installation will associate xar/pkg with Easy 7-Zip automatically
- Double-click on xar/pkg file to open xar/pkg file with Easy 7-Zip
- Alternatively, Right-click on xar/pkg file on Windows Explorer
- Done
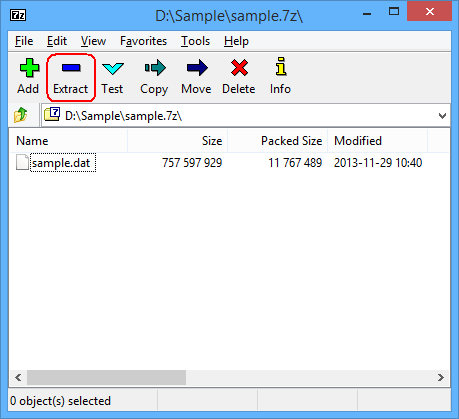
You will see files or folders within the xar/pkg file then, click button Extract to extract the xar/pkg file.
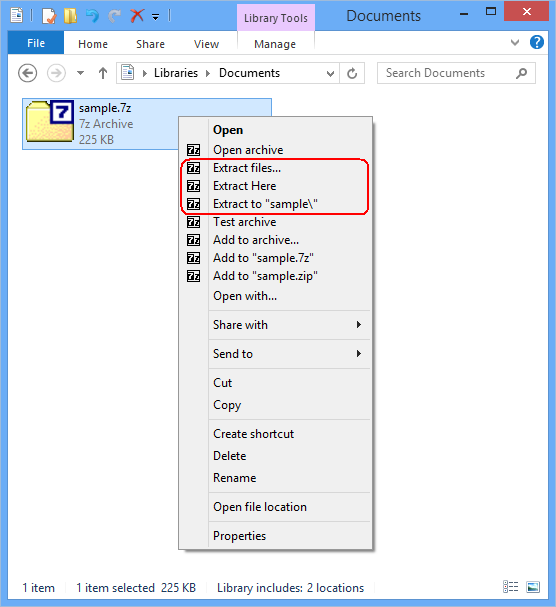
And then, choose Extract files..., Extract Here, or Extract to "folder\" to extract the xar/pkg file.
Easy 7-Zip Download Links:
Open/Extract xar/pkg File on Mac
You can open pkg file directly on Mac. If you want to extract xar/pkg you need to install extra software. B1 Free Archiver opens/extracts xar/pkg file on Mac. B1 Free Archiver is a free software for creating archive folder and extracting archive file. B1 Archiver works on all platforms - Windows, Linux, Mac and Android. The freeware supports most popular formats including xar/pkg.
B1 Free Archiver is compatible with:
- Mac OS X 10.9 Mavericks
- Mac OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion
- Mac OS X 10.7 Lion
- Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard
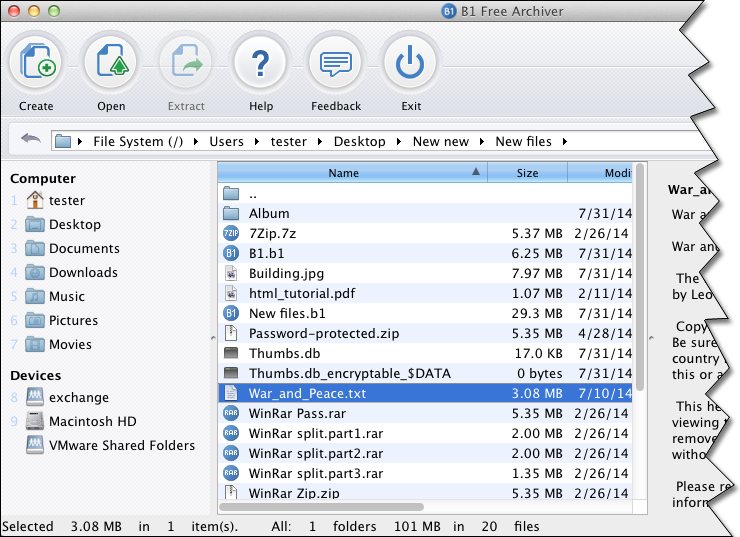
Open/Extract xar/pkg File on Linux
You need to install xar on Linux.
| # wget https://xar.googlecode.com/files/xar-1.5.2.tar.gz # tar zxvf xar-1.5.2.tar.gz # cd xar-1.5.2 # ./configure # make # make install |
If an error "configure: error: Cannot configure without xml2-config" occurs when running configure, please install libxml2-dev. On Debian, type:
| # apt-get install libxml2-dev |
List folders and files in xar/pkg:
| $ xar -tf archive.xar $ xar -tf archive.pkg |
Open/Extract xar/pkg file with xar on Linux:
| $ xar -xvf archive.xar $ xar -xvf archive.pkg |
xar command options:
- -t: Lists an archive
- -x: Extracts an archive
- -v: Print filenames as they are archived
- -f: Specifies an archive to operate on
Alternatively, you can use p7zip to extract xar/pkg file. p7zip is the Unix command-line port of 7-Zip.
Install p7zip-full on CentOS and Fedora
Install p7zip-full on Debian and Ubuntu
| $ sudo apt-get install p7zip-full |
List directories and files in xar/pkg file
| $ 7z l archive.xar $ 7z l archive.pkg |
Extract xar/pkg file with p7zip on Linux
| $ 7z x archive.xar $ 7z x archive.pkg |
Copyright © 2013-2017 James Hoo All rights reserved.
Install Elasticsearch from archive on Linux or MacOSedit
Elasticsearch is as a archive for Linux and MacOS.
This package is free to use under the Elastic license. It contains open source and free commercial features and access to paid commercial features. Start a 30-day trial to try out all of the paid commercial features. See the Subscriptions page for information about Elastic license levels.
The latest stable version of Elasticsearch can be found on the Download Elasticsearch page. Other versions can be found on the Past Releases page.
Download and install archive for Linuxedit
The Linux archive for Elasticsearch v7.9.1 can be downloaded and installed as follows:
Compares the SHA of the downloaded archive and the published checksum, which should output . |
This directory is known as . |
Alternatively, you can download the following package, which includes only Apache 2.0 licensed code: https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.9.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
Download and install archive for MacOSedit
The MacOS archive for Elasticsearch v7.9.1 can be downloaded and installed as follows:
Compares the SHA of the downloaded archive and the published checksum, which should output . |
This directory is known as . |
Alternatively, you can download the following package, which includes only Apache 2.0 licensed code: https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.9.1-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz
Enable automatic creation of system indicesedit
Some commercial features automatically create indices within Elasticsearch. By default, Elasticsearch is configured to allow automatic index creation, and no additional steps are required. However, if you have disabled automatic index creation in Elasticsearch, you must configure in to allow the commercial features to create the following indices:
If you are using Logstash or Beats then you will most likely require additional index names in your setting, and the exact value will depend on your local configuration. If you are unsure of the correct value for your environment, you may consider setting the value to which will allow automatic creation of all indices.
Running Elasticsearch from the command lineedit
Elasticsearch can be started from the command line as follows:
If you have password-protected the Elasticsearch keystore, you will be prompted to enter the keystore’s password. See Secure settings for more details.
By default, Elasticsearch runs in the foreground, prints its logs to the standard output (), and can be stopped by pressing .
All scripts packaged with Elasticsearch require a version of Bash that supports arrays and assume that Bash is available at . As such, Bash should be available at this path either directly or via a symbolic link.
Checking that Elasticsearch is runningedit
You can test that your Elasticsearch node is running by sending an HTTP request to port on :
which should give you a response something like this:
Log printing to can be disabled using the or option on the command line.
To run Elasticsearch as a daemon, specify on the command line, and record the process ID in a file using the option:
If you have password-protected the Elasticsearch keystore, you will be prompted to enter the keystore’s password. See Secure settings for more details.
Log messages can be found in the directory.
To shut down Elasticsearch, kill the process ID recorded in the file:
The startup scripts provided in the RPM and Debian packages take care of starting and stopping the Elasticsearch process for you.
Configuring Elasticsearch on the command lineedit
Elasticsearch loads its configuration from the file by default. The format of this config file is explained in Configuring Elasticsearch.
Any settings that can be specified in the config file can also be specified on the command line, using the syntax as follows:
Typically, any cluster-wide settings (like ) should be added to the config file, while any node-specific settings such as could be specified on the command line.
Directory layout of archivesedit
The archive distributions are entirely self-contained. All files and directories are, by default, contained within — the directory created when unpacking the archive.
This is very convenient because you don’t have to create any directories to start using Elasticsearch, and uninstalling Elasticsearch is as easy as removing the directory. However, it is advisable to change the default locations of the config directory, the data directory, and the logs directory so that you do not delete important data later on.
| Type | Description | Default Location | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
home | Elasticsearch home directory or | Directory created by unpacking the archive | |
bin | Binary scripts including to start a node and to install plugins | ||
conf | Configuration files including | ||
data | The location of the data files of each index / shard allocated on the node. Can hold multiple locations. | ||
logs | Log files location. | ||
plugins | Plugin files location. Each plugin will be contained in a subdirectory. | ||
repo | Shared file system repository locations. Can hold multiple locations. A file system repository can be placed in to any subdirectory of any directory specified here. | Not configured |
You now have a test Elasticsearch environment set up. Before you start serious development or go into production with Elasticsearch, you must do some additional setup:
What’s New in the Mac & Linux Archives?
Screen Shot
System Requirements for Mac & Linux Archives
- First, download the Mac & Linux Archives
-
You can download its setup from given links:


